Definition: A pointer is a variable that stores the address of another variable.
Declaration: In C, every variable must be declared for its type. Since pointer is variable contains address that belong to a separate data type. They must be declared as pointer before we use them.
The general form to declare a pointer is
Syntax: Type *variable-name;
Example: int *p;
Initialization: The process of assigning the address of a variable to a pointer variable is known as initialization.
Syntax: Variable-Name = address of variable;
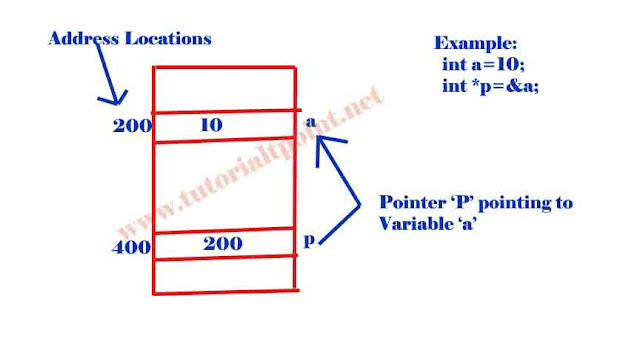
Example: int a=10;
int *p=&a;
Accessing a variable through its pointer:
Once a pointer has been assigned the address of a variable, to access the value of a variable, we use indirection operator(*) in front of pointer variable.
For Example consider the following statements
int a=10; int *p=&a;
Now the following statements shows how to access variable through its pointers.
- printf("%d",a);
- printf("%d",*p);
- printf("%d",&a);
- printf("%d",p);
- printf("%d",&p);
The first statement prints the value stored in 'a' as 10
The second statement also prints the value of 'a' through it pointer.
The third line prints the address of variable 'a'
The fourth line prints the content of pointer variable i.e what pointer stored as "200"
The fifth line prints the address of pointer variable as"400"
For better understanding of the printf statements out put observe the above diagram.

0 comments :
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.